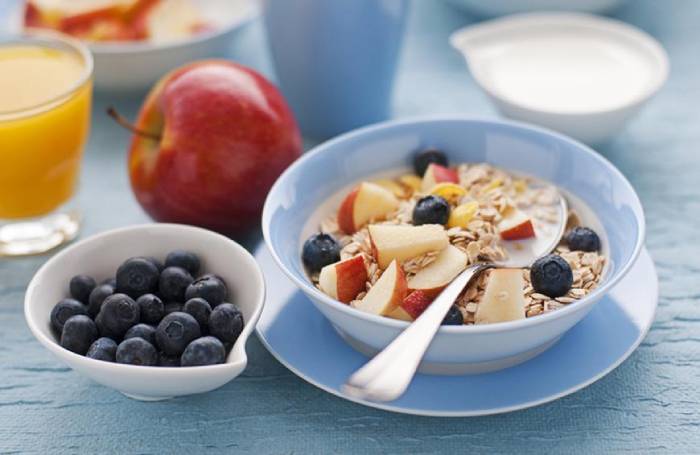
Metabolism is the process by which the food you eat is turned into fuel and used to power your activities. To breathe, think, digest, circulate blood, and stay warm in the cold and cool in the hot, human bodies require energy. The holy grail of weight loss has long been thought to be increasing metabolism.
Try these easy methods to increase your metabolism-
Cardio
When it comes to traditional cardio (not including HIIT), you only burn calories while you’re exercising; however, HIIT and strength training enhance your metabolism for hours afterward, increasing fat burn for far longer than the time you worked out.
Breakfast should be a metabolism booster-
Rather to focusing on quantity, the kind of items on your breakfast plate have a big impact on your metabolism. If you want to rev up your system, a study found that low-GL (therefore low-sugar) and high-protein foods should be included in your morning. Choose a savoury dish with a lean protein source, such as chicken or eggs.
Drink a lot of water-
Drink water instead of sugary drinks! Studies show that people who drink more water burn more calories. Increasing your water intake can help your metabolism speed up. According to studies, drinking 0.5 litres of water every hour might boost resting metabolism by 10–30%. Additionally, drinking 1–2 glasses of water before meals may help you feel full and eat less calories.
Stand up-
Because sitting for long periods of time burns fewer calories, standing up is critical for people who want to improve their metabolism. In fact, research show that breaking up long periods of sitting can help to reduce health risks and enhance metabolism. Investing in a standing desk or taking small pauses to stand up and walk around during the day may be beneficial.
Increase your fibre consumption-
Increasing your fibre intake may aid weight loss. How so? Experts believe that eating a high-fiber diet increases metabolism because fibre is indigestible. Fibre comes in two types: soluble fibre, which absorbs water as it digests and keeps you fuller for longer, and insoluble fibre, which simply passes through the system and aids in the passage of food.
Although it tries, the body is unable to digest fibre. When digesting and excreting fibre, the body expends more calories than when digesting and excreting other nutrients. As a result, high-fibre diets require more energy to digest than refined carbohydrate diets.
Green tea, please-
Green tea has been shown to increase metabolic rate by 4–5%. It offers a number of health benefits, but it also contains a plant chemical known as EGCG, which, according to research, encourages your body to burn fat. Their metabolism-boosting properties are thought to aid in avoiding the dreaded weight loss plateau induced by a slowing metabolism.
Several studies, however, have discovered that these teas have no impact on metabolism. As a result, their impact may be confined to a small group of people.
Get enough sleep-
Experts say that sleep has little effect on metabolism. However, a lack of sleep can induce hormonal imbalance, leading in a dysregulation of hunger and appetite hormones.
Sleep deprivation might make you feel hungry during the day and less satisfied when you eat. Furthermore, it might make you crave sweet foods. As you can see, sleep deprivation has little effect on metabolism, but it does make it much more difficult to eat in a way that leads to a healthy body weight.
Consume a varied diet-
Proteins need more energy to digest, absorb, and use than fats, but this does not mean that specific foods will slow down your metabolism. As a result, consuming more protein and less fat will cause a person to burn more calories. It will take less calories to digest and absorb a meal if the diet is strong in fat. Thermic impact of food is the term for this. This does not mean that you should eat a low-fat diet; rather, you should avoid a high-fat, high-sugar diet in favour of a diet rich in lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, complex carbs, and healthy fats.
- March Madness 2025: Printable Bracket, Game Schedule & How to Watch - March 13, 2025
- March Madness Miracles: Worst Records to Get an NCAA Tournament Bid - March 13, 2025
- NCAA DI Wrestling Championships 2025: How to Watch, Brackets & Selection Info - March 13, 2025